One of the critical factors you have to consider when shopping for a dirt bike or even an ATV is the engine type. Therefore, understanding how a two-stroke engine works can go a long way in getting an ideal machine for your use.
A two-stroke engine works by combining different functions into one piston movement; during the upward movement, a mixture of air and fuel is drawn into the combustion chamber. During the downward movements of the piston, a mixture of fresh air and fuel is compressed and flows to the combustion chamber, flushing out the burnt gasses.
To understand the 2-stroke engine, you need to closely examine various aspects, including differentiating between the 4-stroke engine and the 2-stroke engine.
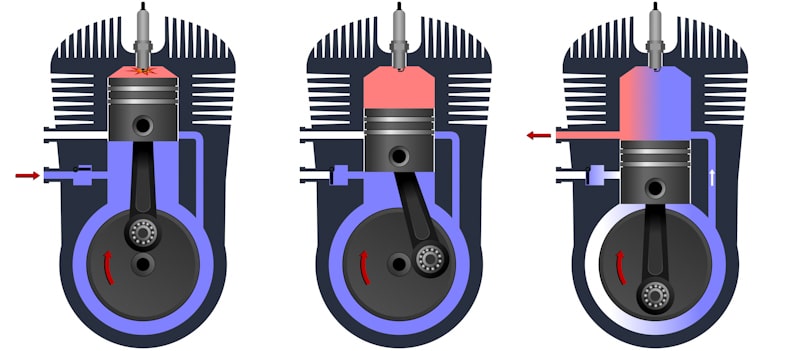
Essential Engine Terms You Should Know
To better comprehend how a 2-stroke engine works, it is vital to educate yourself on various essential terms concerning its functionality.
Stroke
The term stroke is derived from the concept of piston movement in the combustion chamber. A single stroke is the movement of the piston to complete the four functions necessary for an engine to function.
Camshaft
The camshaft is another essential component of an engine. It is responsible for the opening and closing the valves in the combustion chamber. The camshaft is closely linked to the crankshaft and must be timed accurately to close and open ports at the right moments.
Ports
2-stroke engines depend on ports, which work with the piston to create a sleeve valve system. The ports play a crucial role in allowing the spent fuel to exit the chamber while allowing a fresh mixture to get into the chambers.
What is the difference Between a 2-stroke and a 4-stroke Engine?
If you wonder what kind of engine you should get for your dirt bike, then it is good to note that understanding the difference between the 2-stroke engine and the 4-stroke engine will make your work pretty easier.
As the name implies, a four-stroke engine is a piston that makes four strokes to complete one full cycle. In other words, when the piston moves downwards in the cylinder, it reduces the cylinder's pressure, resulting in the drawing of fuel and air into the cylinder. The piston goes back, compressing the mixture of the air and fuel, after which a spark ignites the fuel. As a result of the initiated combustion, the piston goes back in a power stroke. Finally, the piston pushes the burnt gasses out by going back up.
On the other hand, a 2-stroke engine follows all the same steps, but the only difference is that it completes in two piston strokes. The simplest 2-stroke engine uses the crankcase and the underside of the moving piston to serve the role of a fresh charge pump.
How a 2stroke Engine Works
If you are not sure how a 2-stroke engine works, you need to familiarize yourself with the different parts of a 2-stroke engine, which include;
- Fuel injector
- Cylinder
- Cylinder head
- Spark plug
- Crank
- Crankshaft
- Piston
- Connecting road
- Piston rings
- Ports – inlet, transfer, and exhaust
The Stages of a 2-stroke Engine
The 2-stroke engine has two essential cycles; Suction and compression (First Stroke) During the first cycle of a 2-stroke engine, the piston moves from the bottom center to the top with all three ports closed. The spark plug ignites to create a power stroke. The created power is transferred to the crankshaft with the assistance of the connecting rod. Also, a partial vacuum in the crankcase opens the inlet port to allow the air-fuel mixture inside.
Power and Exhaust Stroke (Second stroke)
During the second stroke, the piston moves downwards, and the inlet port is closed. When the piston moves downward, it pushes the fuel-air mixture, making the charge from the crankcase come out through the transfer port. Since the exhaust port is open, most exhaust gas escapes from the cylinder. Both the parts of a 2-stroke petrol engine and a diesel engine work this way.
2 Stroke Engine Diagram
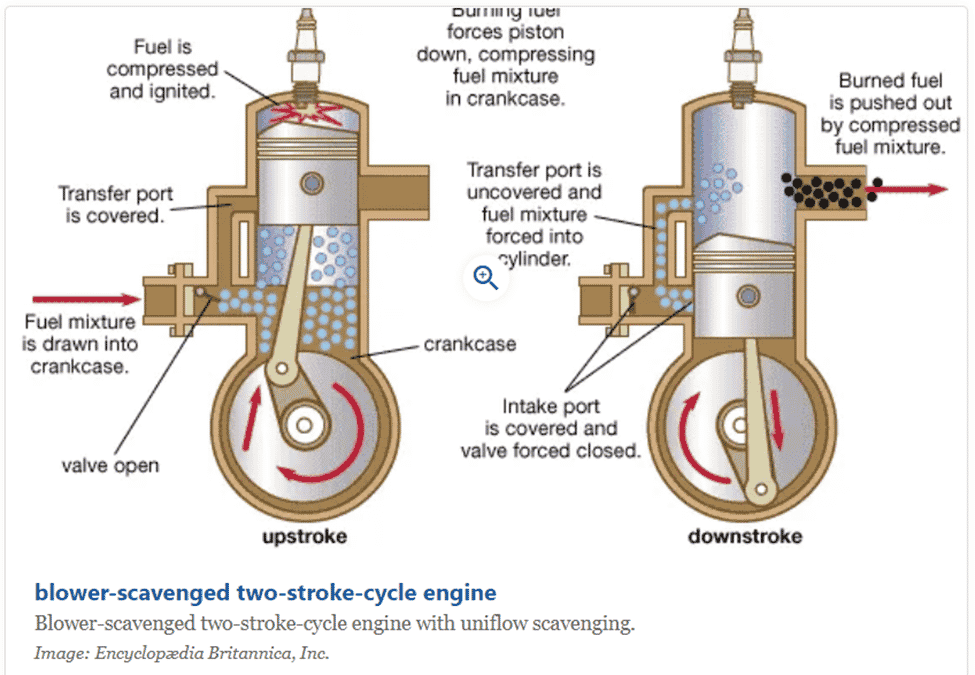
The first 2-stroke engine came into existence in 1878. In the original 2-stroke engine, the four-stroke compression and power stroke are performed without the exhaust strokes and the inlet, hence the need for one crankshaft revolution to complete the cycle.
Two Stroke Engine
The manageable size and the power of a two-stroke engine make it ideal for various small-scale applications. You can find a 2-stroke engine on,
- Dirt bikes
- RC toys
- Small watercraft
- Chainsaws
- Landscaping Tools
Advantages and Disadvantages of Two-Stroke Engines
Advantages
- If you keep the dimensions constant, the power developed by a 2-stroke engine is twice that of a four-stroke engine.
- Less work is required to overcome the friction of suction and exhaust
- Low maintenance cost
- Easy to start
- Simple mechanism
- It has few moving parts meaning that it is compact and durable
- No oil sump is required for lubrication, meaning that petrol can be helpful in all positions
- It is lighter by 30% when compared to a 4-stroke engine
- High power to weight ratio
Disadvantages of two-stroke Engine
- Reduced volumetric efficiency makes the high-speed 2-stroke engine less efficient
- Less effective compression resulting from several ports for intake and exhaust
- High rate of consumption of lubricating oil
- Inefficiency when handling high loads due to dilution of charge
- Unstable idling
How to Improve the Performance of a Two-Stroke Engine
If you want to improve the efficiency of your two-stroke engine, you need to understand that there are several options that you can adopt to achieve your objectives. In almost all the options, the Q factor is enhanced, implying that the engine delivers more output. Here are some of the options that you can embrace.

Increasing the Cubic Capacity
Increasing the cubic capacity is one of the simplest ways of enhancing the performance of your engine. You will need to consider increasing the stroke or the bore, or even both, to accomplish this.
However, it is good to note that increasing the stroke is the easy option. This is because it is possible to purchase a crank billet and grind the end journal off to foster a longer stroke. It would help to remember to improve the cooling system and the clutch.
Increasing the Mean Effective Pressure
Increasing the mean effective pressure can also prove significant when it comes to increasing the engine's performance. To accomplish this modification, you will need to deploy two methods: increasing the compression and improving the gas flow.
Increasing the compression improves fuel utilization and fosters a higher mean effective pressure.
Inspect the Exhaust System
It is good to acknowledge that your two-stroke engine will never realize its full potential if the exhaust has resistance problems. Therefore, getting rid of any problems in the exhaust will prove critical in enhancing the performance of your engine.
Get the Cylinder Ported
Many people who interact with two-stroke engines report significant improvement in the performance of their engines after performing this procedure. Therefore, if you have never tried making changes to your port, you may want to try it. The exhaust, intake, and transfer ports should be shaped and enlarged as a rule of thumb.
Such alteration benefits the engine a lot, and they have proved to be essential in improving the engine's performance. Other modifications that you may consider to make your engine better include;
- Checking the ignition timing
- Install a reed valve to boost the horsepower
- Reduce the squish gap
- Down the jet engine
Conclusion
A two-stroke engine boasts numerous benefits, including compactness, lightweight, simplicity, efficiency, and easy maintenance. However, to make the necessary modifications to enhance the performance of your engine, you will need to have a good understanding of how a two-stroke engine works.
Also read: 2 Stroke vs. 4 Stroke Dirt Bikes, Main Difference
Shawn Manaher loves to play with new toys and dive into new hobbies. As a serial entrepreneur, work definitely comes first but there is always room for hobbies.

![How Does a 2 Stroke Engine Work? [COMPLETE GUIDE]](https://hobbynation.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/how-does-a-2-stroke-engine-work.jpg)